Spin Orbit Coupling
In order to perform fully relativistic calculation:
(A) Full relativistic effects can only be applied in non-collinear calculations.
scf.SpinPolarization NC # On|Off|NC
When the option NC is specified, wave functions are expressed by a two
component spinor, and initial spin orientation of each site should be provided:
<Atoms.SpeciesAndCoordinates # Unit=Ang
1 Mn 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 8.0 5.0 45.0 0.0 45.0 0.0 1 on
2 O 1.70000 0.00000 0.00000 3.0 3.0 45.0 0.0 45.0 0.0 1 on
Atoms.SpeciesAndCoordinates>
| Col | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | sequential serial number |
| 2 | species name |
| 3 | x-coordinate |
| 4 | y-coordinate |
| 5 | z-coordinate |
| 6 | initial occupation for up spin |
| 7 | initial occupation for down spin |
| 8 | Euler angle, theta, of the magnetic field for spin magnetic moment |
| 9 | Euler angle, phi, of the magnetic field for spin magnetic moment. Also, the 8th and 9th are used to generate the initial non-collinear spin charge distribution |
| 10 | the Euler angle, theta, of the magnetic field for orbital magnetic moment |
| 11 | the Euler angle, phi, of the magnetic field for orbital magnetic moment |
| 12 | switch for the constraint schemes specified by the keywords scf.Constraint.NC.Spin and scf.NC.Zeeman.Orbital. 1 means that the constraint is applied, and 0 no constraint. |
| 13 | switch for enhancement of orbital polarization in the LDA+U method, on means that the enhancement is made, off means no enhancement. |
(B) Use -dependent pseudopotential, i.e., it incorporates full relativistic correction.
(C) Turn on the soc flag:
scf.SpinOrbit.Coupling on # On|Off, default=off
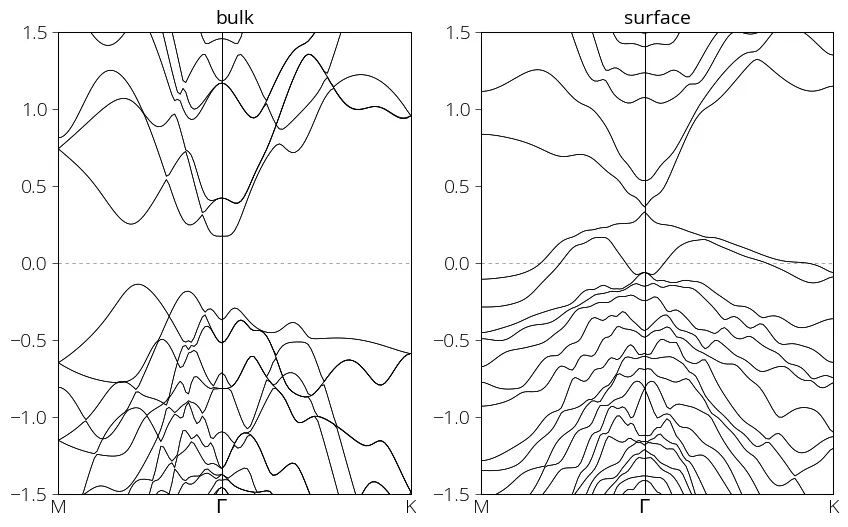
Bulk and surface bands for Bi2Se3
Here we compare the bulk and surface electronic structure of topological insulating Bi2Se3. In both cases we consider noncollinear magnetism with spin orbit coupling. In case of slab calculation 10 Å vacuum is introduced among the layers.